HYDRUS-2D is
a finite element model for simulating the two-dimensional
movement of water, heat and multiple solutes in unsaturated,
partially-saturated or fully-saturated media.
The software package also
includes a parameter optimization module for inverse
estimation of soil hydraulic parameters and solute transport
parameters. The model is supported by an interactive
graphics interface for data preprocessing and comprehensive
presentation of results. The modeling environment may
optionally include a mesh generator, MESHGEN-2D, for
unstructured finite element grids.
Extensive context-sensitive, online Help is part
of the interface.
|
|
Solution
Method:
|
 click.to.enlarge
click.to.enlarge
|
Water Flow:
- The program numerically
solves Richards' Equation for variably saturated water
flow
- The
flow equation includes a sink term to account for water
uptake by plant roots
- Boundary
conditions can be constant / time-varying hydraulic head
or flux or boundaries controlled by atmospheric
conditions. The code can also handle seepage face
boundaries and free drainage boundary conditions.
|
 click.to.enlarge
click.to.enlarge
 click.to.enlarge
click.to.enlarge
|
Heat
and Solute Transport:
- The program applies Fickian-base
advection-dispersion equations for heat and solute
transport
- Heat transport equation
considers both conduction and convection
- Solute transport equations consider:
- advective-dispersive transport in
the liquid phase
- diffusion in the gaseous phase
- nonlinear and/or nonequilibrium
reactions between the solid and liquid phases
- linear equilibrium reactions
between the liquid and gaseous phases
- zero order production
- two first-order degradation
reactions:
- degradation reactions
independent of other solutes
- degradation reactions which
couple the solutes involved in sequential
first-order decay reactions
- The solute transport code supports
constant / time varying concentration and concentration
flux boundary conditions
|
Applications
Include:
|
 click.to.enlarge
click.to.enlarge
|
- Agricultural
- Irrigation management
- Drip irrigation design
- Sprinkler irrigation design
- Tile drainage design - flow to a
drainage system
- Crop grow models
- Salinization and reclamation
processes, salt leaching
- Movement of pesticides; nonpoint
source pollution
- Seasonal simulation of water flow
and plant response
|
 click.to.enlarge
click.to.enlarge
|
- Nonagricultural
- Risk analysis of contaminant
plumes
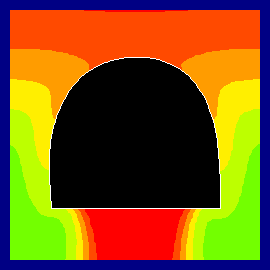
- Tunnel design - flow around
burried objects
- Highway design - road
construction - seepage
- Stochastic theory - solute
transport in heterogeneous media
- Lake basin recharge analysis
- Interaction between groundwater
aquifers and streams
- Environmental impacts of drawdown
of shallow water tables
- Analysis of cone permeameter and
tension infiltrometer experiments
|
HYDRUS-2D Key
Features:
click to enlarge
|
Versatile
Flow Regime HYDRUS-2D can
handle flow regions delineated by irregular boundaries
and the flow region may be composed of nonuniform
soils with local anisotropy.
|
click to enlarge
|
Hysteresis HYDRUS-2D
incorporates hysteresis scaling the
drying scanning curve from the main drying curve and
the wetting drying curve from the main wetting curve.
|
click to enlarge
|
Hydraulic
Variability HYDRUS-2D
implements a scaling procedure to approximate
hydraulic variability by means of a set of linear
scaling transformations which relate the individual
soil hydraulic characteristics to those of a reference
soil.
|
click to enlarge
|
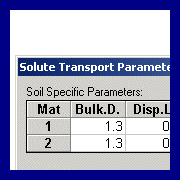
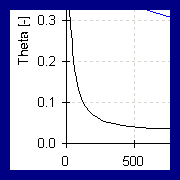
Parameter
Estimation HYDRUS-2D
uses a Marquardt-Levenberg type parameter estimation
for inverse estimation of selected soil hydraulic
properties and/or solute transport parameters from
observed data such as pressure heads or
concentrations.
|

click to enlarge
|
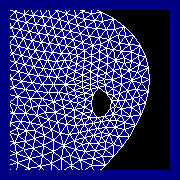
Automatic
Mesh Generation HYDRUS-2D
provides an optional mesh generation program
MESHGEN-2D for automatic construction of unstructured
grids. This complementary program allows the
user to generate and edit a finite element grid within
the HYDRUS-2D shell.
|
|
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
|
User-Friendly
Graphics Interface A Microsoft
Windows-based graphical user interface manages the input data
required to run HYDRUS-2D, all spatially distributed parameters, such as soil
type, soil layer, root water uptake distribution and the initial
conditions for water, heat and solute movement, are specified in
a graphical environment. The HYDRUS-2D shell also handles
nodal discretization and
editing, parameter allocation, problem execution and
visualization of results.
|
|
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
|
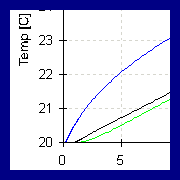
Visualization
of Results / Post-Processing
Output can
be examined within the HYDRUS-2D shell. Graphical output includes:
distribution of the pressure head, water content,
temperature and concentration through time at set
observation nodes. Output also includes soil
hydraulic properties and many variable-vs-time plots, such as
water boundary heads, root water uptake and actual, potential and cumulative water
or solute fluxes across boundaries or
leaving the root zone.
|
Developers:
J.Simunek, M.Th. van Genuchten (U.S. Salinity Laboraty, USDA/ARS,
Riverside, California)and M. Sejna (PC Progress, Prauge, Czech
Republic)
There's more
Click here
for additional information on HYDRUS-2D
Back
to top of page
|
MESHGEN-2D is
a Windows Application used in finite element modeling to
generate triangular-element meshes.
- The program can be
used on its own or with the programs HYDRUS-2D and CochemFlow.
- MESHGEN-2D
enables automatic mesh generation based on
Delaunay triangulation.
- All
information about a mesh can be exported to a text file in
described simple format.
- The
MESHGEN-2D user interface is
intuitive and easy to learn.
|
|
Key
Features:
|
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
|
Versatile 2D
Domain
Meshgen-2D enables
the design of 2D meshes constructed from arbitrary continuous shapes
bounded by poly-lines, arcs and splines.
The domain can have any number of holes, internal curves
or internal points. All
geometric objects can be entered and edited graphically or
numerically and coordinates of very complicated shapes can be
imported from other programs.
|
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
|
Vast Grid Size
The mesh
can be refined along any nodes or curves and meshes can be
very fine, the mesh size is virtually unlimited allowing more
than 2,000,000,000 triangles.
|
Advanced
Features:
|
 click.to.enlarge
click.to.enlarge
|
Mesh
Stretching
This feature enables
the user to define the degree of mesh anisotropy in a general
direction. This
feature is useful when a
different spatial step is required in the X and Y-directions.
|
 click.to.enlarge
click.to.enlarge
|
Mesh
Smoothing Parameters
Several options are
available to optimize mesh smoothness, default values usually
yield good results but the user is given the option to change
these values.
|
|
Periodical
Boundary Conditions
Boundary
conditions can be defined on two parts of a boundary curve that
are exactly the same and differ from each other just by a vector
of translation. The
periodical condition requires a special mesh points distribution
along the boundary; each point must have a corresponding
‘periodical point’ and their positions differ by the vector
of periodical translation.
If the user specifies periodical conditions, the program
automatically checks and corrects the mesh to satisfy these
periodical conditions.
|
|
There's more
Click here
for additional information on MESHGEN-2D
Back
to top of page
|
|
HYDRUS-1D is a Microsoft Windows-based
modeling environment used to simulate the one-dimensional
movement of water, heat and multiple solutes in unsaturated,
partially-saturated or fully-saturated porous media.
HYDRUS-1D
is a finite element model; it numerically solves the Richards’
equation for variably saturated water flow and Fickian-based
advection-dispersion equations for heat and solute transport.
The model includes a parameter optimization algorithm for
inverse estimation of a variety of soil hydraulic and/or solute
transport parameters. The
model is supported by an interactive graphics-based interface
for data-preprocessing, discretization of the soil profile and
graphic presentation of results.
Key
Features:
Water Flow: The flow
regime
may be made up of nonuniform soils and can occur in the
vertical, horizontal or an inclined direction.
The model can deal with constant or transient
water flow with user-defined head and flux boundaries,
boundaries controlled by atmospheric conditions and free
drainage boundary conditions.
Soil surface boundary conditions may change during a
simulation from a predetermine flux to a head type condition
or vice versa.
The flow equation also incorporates a sink term to
account for water uptake by plant roots.
Heat and Solute
Transport: The heat transport equation considers conduction as well
as convection with flowing water. The
solute transport equations consider
advective-dispersive transport in the liquid phase, and
diffusion in the gaseous phase.
The transport equations also include nonlinear and/or
nonequilibrium reactions between the solid and liquid phases,
linear equilibrium reactions between the liquid and gaseous
phases, zero order production and two first order degradation
reactions; one which is independent of other solutes and one
which provides the coupling between solutes involved in
sequential first-order decay reactions.
The solute transport code supports constant and
temporally variable user-defined concentration (first-type) and
concentration flux (third-type) boundary conditions.
Hysteresis:
The HYDRUS-1D code includes an empirical model which incorporates hysteresis
by scaling new drying or wetting scanning curves from the main drying
or wetting curve.
Unsaturated soil hydraulic properties:
The unsaturated soil hydraulic properties are described using
van Genuchten, Brooks and Corey and modified van Genuchten type
analytical functions.
Hydraulic
variability: The hydraulic variability within a given soil profile is approximated
using a scaling procedure through a set of linear
transformations which relate the individual soil hydraulic
characteristics to those of a reference soil.
Parameter
Estimation: HYDRUS-1D uses a Marquardt-Levenberg type parameter estimation
technique for reverse estimation of selected soil hydraulic
and/or solute transport and reaction parameters from measured
transient or steady-state flow and/or transport data.
The procedure allows several unknown parameters to be
estimated from observed water contents, pressure heads,
concentrations and/or instantaneous or cumulative boundary
fluxes (i.e.
infiltration or outflow data).
|
|
 click.to.enlarge
click.to.enlarge
|
 click to enlarge
click to enlarge
|
|
User
Interface:
·
A Microsoft
Windows-based graphical user interface manages the input data
required to run HYDRUS-1D, as well as for nodal discretization and
editing, parameter allocation, problem execution and
visualization of results.
·
All spatially distributed parameters, such as soil
type, soil layer, root water uptake distribution and the initial
conditions for water, heat and solute movement, are specified in
a graphical environment.
·
A user can optimize the thickness of different
elements by graphically editing the location of discretization
nodes.
·
Both input and output can be examined using
graphical tools.
·
The HYDRUS-1D shell program translates all
geometric and parameter data into the HYDRUS input form.
·
Post-processing is also carried out in the shell.
Graphical output includes:
distribution of the pressure head, water content, water
and solute exchange fluxes, root water uptake, temperature and
the concentration in the soil profile at predetermined times.
Output also includes variable-vs-time plots, such as
actual, potential and cumulative fluxes across boundaries or
leaving the root zone.
·
Observation points can be added anywhere in the
profile to obtain graphical output for the water content,
pressure head, temperature and/or concentration.
·
Extensive context-sensitive, online Help is part
of the interface.
|
|
Back
to top of page
|
GroundwaterSoftware.com is brought to you
by
Environmental
Software Online, LLC
520 Chicopee Row, Groton, MA 01450 USA
Tel: (978) 448-5818 Fax: (978) 772-0595
E-Mail: info@groundwatersoftware.com
|



















